(425) 522-4110
Brand New!
Cracking Open the Payments Orchestration Layer
Payments orchestration has captured the industry’s attention because of the value-added benefits provided to revenue and expense management. Performance is only as good as the support given to it and usually, that support means access to engineering. Optimizing payments requires valuable engineering resources, and because of that, fully developing a POL will always be resource-constrained. Each merchant must draw the line between MVP and a platform that doesn’t deliver on the promised benefits.
This white paper clarifies the ambiguity around the Payments Orchestration Layer (POL) definition and helps readers resolve the buy vs. build conundrum by identifying the requirements to achieve a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and providing effort estimates to achieve MVP.
Enhancing the Customer Experience
Taking the Plunge and Building a Switch
Merchants need a payments switch to effectively use a multi-Payment Service Provider environment. T-Mobile U.S. and RPGC discuss the benefits, requirements, and build/buy decisions that go into the technical components when implementing a switch.
The Paypers: The Merchant’s Need for Payments Orchestration
Customers need to be offered the ability to use the payment methods and currencies they want and when they pay, the authorisation needs to succeed. not meeting this premise means there has been an undercapitalisation of the efforts from marketing, operations, sales, product, engineering and finance. So why can’t a single Payment service Provider (PSP) service all of a merchant’s needs? The answer’s inside!
Published in the Paypers 2019 Payment Method Report.
Payments as a Strategic Asset
Payments makes up 2 – 5% of top-line operating costs, but is often a function hidden within finance or operations. The lack of support leads talented people to migrate into other facets of a company as there is no clear career path upwards. This is a waste of talent development! As a company’s revenue gathering function, payments requires a ‘seat at the table’ to best support revenue growth projects, identify cost saving opportunities and provide valuable input on enhancing the customer experience. In this presentation, RPGC advocates the strategies that can bring additional visibility to the function so that value can be demonstrated across the entire organization.
Lowering Costs
Why Should Merchants Care About Faster Payments?
Real Time Payments have arrived in the U.S. Together with the Federal Reserve of Chicago and The Clearing House, RPGC discusses the background of faster payments in the U.S., the new RTP rails and how merchants can leverage this new technology at the Point-of-Sale.
Digital Transactions: How Online Merchants Can Make Durbin Pay Off
In 2011 when the Durbin Amendment was fresh law, RPGC identifies the benefits of PIN-less debit routing for e-commerce and m-commerce merchants.
Digital Transactions: The Durbin Amendment and the Future of Interchange
Five years after the implementation of the Durbin Amendment, consumers still saw rising costs and the equilibrium lawmakers sought, was not found. RPGC examines what went wrong, what can be done to alleviate these rising payments costs and argues against the repeal of the flawed Durbin Amendment.
Defining a Multi-Currency Strategy
Global eCommerce and multi-currency payments are here now, companies that have implemented a well thought out cross-border currency capability are already enjoying increased sales and improved margins. Implementing a multi-currency strategy should not be undertaken lightly as its impact, particularly to the technical, accounting, and finance functions is far-reaching.
This white paper examines the major attributes of multi-currency e-commerce and provides a planning checklist for merchants to implement a strategy for acceptance of multiple currencies. It describes how different merchant sales models impact multi-currency handling requirements, identifies factors that merchants must take into account in order to minimize implementation risk, and reviews, in general terms, some of the commercial solution options available.
The Merchant Cost of Fraud
The Cost of Fraud is increasing, but how do you calculate it for upper management? Use this presentation as a quick guide for combining your costs of chargebacks, fraud claims, manual review, technology and, false positives when articulating a business case.
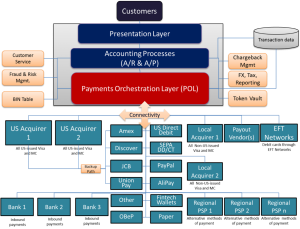
Payments Orchestration
Cracking Open the Payments Orchestration Layer
Payments orchestration has captured the industry’s attention because of the value-added benefits provided to revenue and expense management. Performance is only as good as the support given to it and usually, that support means access to engineering. Optimizing payments requires valuable engineering resources, and because of that, fully developing a POL will always be resource-constrained. Each merchant must draw the line between MVP and a platform that doesn’t deliver on the promised benefits.
This white paper clarifies the ambiguity around the Payments Orchestration Layer (POL) definition and helps readers resolve the buy vs. build conundrum by identifying the requirements to achieve a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) and providing effort estimates to achieve MVP.
Payments Orchestration Layer: Necessary functionality in the payments stack
This white paper presents the business case for enterprise merchants to utilize an abstraction layer that consolidates payments functionality into a single business-oriented architecture. The payments ecosystem is complex, exacerbated by fragmentation. No single Payment Service Provider can fully service every market and each merchant must develop the exact same logic and requirements to comply with the changes imposed by the card schemes. In-house solutions are typically engineering driven and since payments expertise is rare among engineers, most legacy architecture is manual and burdensome on IT.
The proposed business-oriented architecture, called a Payments Orchestration Layer (POL), addresses these above challenges. POLs are built on four key pillars of global connectivity, smart routing, real-time ledgers and end-user tools. This architecture allows merchants to use payments to further pursue their goals of enhancing the customer experience, lowering costs and supporting market growth.
Supporting Market Growth
Payments in South Korea
Looking for a quick primer on payments in South Korea? Look no further.
Presented at MRC 2017.
RFP Management for Payments
Running payments RFPs are difficult. The market is fragmented with several different solution provider types that can create easy misinterpretations of an potential provider’s capabilities. RPGC’s RFP process is streamlined so that you get your requirements met at a fair market rate and in a timeline of 8 – 10 weeks. For you bold readers, feel free to use this document as your ‘how-to’ reference guide!
PSD2 & Open Banking: A Primer
Wonder what XS2A, ASPSP and Competent Authorities are? Learn about the commercial, operational and technical implications of this brand new banking world.
Digital Transactions: Stop Pushing Payments, Start Building Commerce
In 2012, many merchant apps were designed solely to accept payments. RPGC advocated that apps must act as a customer engagement tool first. Payments is a means of achieving this goal, not the end goal.
Building a Merchant Payments Architecture
Establishing a payments infrastructure isn’t easy, nor is articulating that vision to the C-level. RPGC and Microsoft discuss the requirements for a merchant payments infrastructure that demonstrates value to cost, market growth and the customer experience.
Thought Leadership
Payment Insecurity: How Visa and Mastercard Use Standard Setting to Restrict Competition and Thwart Payments Innovation
During 2019, RPGC conducted research under the sponsorship of the Secure Payments Partnership (SPP) regarding EMVCo’s role as a standards-setting body. The result of this year of research was this whitepaper.
While EMVCo calls its product outputs specifications, we will use the term “standards.” Since the card brands (e.g. Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, JCB, UnionPay) decree these specifications as the means for participation in their networks these specifications become de facto standards. Because the entire U.S. industry must invest and comply with these specifications, EMVCo specifications, developed jointly with the card brands in an orchestrated strategy, are effectively standards.
This paper’s operating principle is that standards that exclude certain payment instruments or prevent participants from freely routing payment transactions are collusive, harmful to the U.S. payments industry, and may violate federal law.
What’s inside?
- Part I includes this introduction, an executive summary, a review of standards and standards-setting organizations, and finally a high-level overview of EMVCo’s organization and its standards-development processes.
- Part II includes an in-depth review of each of the standards for which EMVCo is currently responsible: EMV chip & pin, Near-Field Communication, Network Tokenization, and 3D-Secure 1. This in-depth review covers the standards-development process (to the extent that it is documented), market context and commentary based on interviews with leading industry experts.
- Part III includes an in-depth review of currently deploying solutions 3D-Secure 2 and Secure Remote Commerce.
- Part IV concludes that EMVCo is not an appropriate organization to develop standards that have such a high impact on the U.S. payments industry. Our research spotlights the nature of EMVCo and its relationship with card companies as a tool to deliver standards that further their market dominance.
Next Generation Payments
Presented at the 2016 Chicago Payments Symposium by the Federal Reserve, RPGC examines how mobile payments, same day ACH, Real Time Payments and PSD2 affect the existing layers within the payments ecosystem.
The Need for Real-Time Payments in the US
When compared with other payment environments around the globe, US low value payments systems are slow and inefficient. In the US, calls for innovation and modernization of the payments infrastructure to accelerate the speed of payments have gone unheeded, leaving Consumers frustrated and Businesses at a competitive disadvantage in the global arena…